XEN1101 (FOS)
XEN1101 is a novel, potent Kv7 potassium channel opener being developed for the treatment of epilepsy, major depressive disorder, or MDD, and potentially other neurological disorders.
XEN1101 for Focal Onset Seizures (FOS)
Xenon’s XEN1101 Phase 3 epilepsy program includes two identical Phase 3 clinical trials, called X-TOLE2 and X-TOLE3, that are designed closely after the Phase 2b X-TOLE clinical trial. Xenon anticipates patient enrollment in X-TOLE2 will be completed in late 2024 to early 2025.
For those living with either focal-onset seizures (or primary generalized tonic-clonic seizures), you may be eligible to enroll one of our ongoing Phase 3 clinical trials. Learn more here.

X-TOLE2 and X-TOLE3 are two identical Phase 3, multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials to evaluate the clinical efficacy, safety, and tolerability of XEN1101 as adjunctive treatment in adults aged ≥18 years diagnosed with FOS who are taking 1 to 3 ASMs.
Approximately 360 patients will be randomized 1:1:1 for once-daily dosing of XEN1101 (15 mg), XEN1101 (25 mg) or placebo in each trial once-daily with food. Eligibility criteria include adults aged 18 to 75 years old taking one to three anti-seizure medications with a seizure frequency of ≥4 seizures per month at baseline.
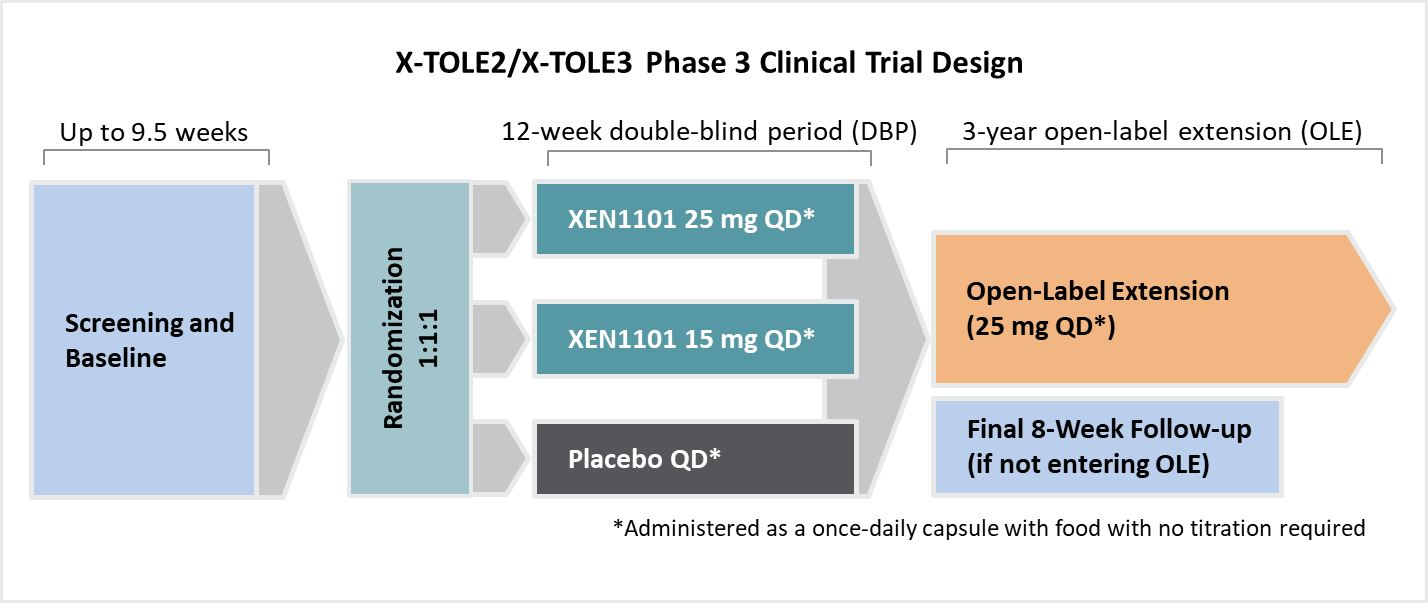
Screening/baseline period: Up to 9.5 weeks duration to assess the frequency of seizures.
Double-blind period (DBP): 12 weeks duration. There is no titration period.
Follow-up period: 8 weeks duration after the last dose of study drug for subjects who do not complete the 12-week DBP or who complete the DBP but do not enter the OLE study.
On completion of the double-blind period in X‑TOLE2 or X‑TOLE3, eligible patients may enter an open-label extension study for up to three years.13
About Epilepsy and Focal Onset Seizures
Epilepsy is a chronic neurological disorder, the hallmark of which is recurrent, unprovoked and unpredictable seizures. Individuals are diagnosed with epilepsy if they have two unprovoked seizures (or one unprovoked seizure with the likelihood of recurrent seizures) that were not caused by a known and reversible medical condition.
Seizures are generally described in two major groups: focal onset seizures, or FOS, and generalized onset seizures. FOS are the most common type of seizure experienced by people with epilepsy. FOS are localized within the brain and can either stay localized or spread to the entire brain, which is typically categorized as a secondarily generalized seizure.
FOS account for approximately 60% of seizures in the U.S., which results in a total FOS patient population of approximately 1.8 million patients.